
THCP, a phytocannabinoid naturally present in cannabis and similar to THC, the main psychoactive component of cannabis, was recently identified in 2019 by a group of Italian researchers. It is one of 120+ cannabinoids that have so far been discovered in the cannabis plant, with many more potentially yet to be discovered.
What particularly intrigues the cannabis community is the possibility that THCP could have a greater influence on the psychoactive properties of a cannabis variety than THC itself. This article explores the meagre information currently available on this recently discovered cannabinoid.
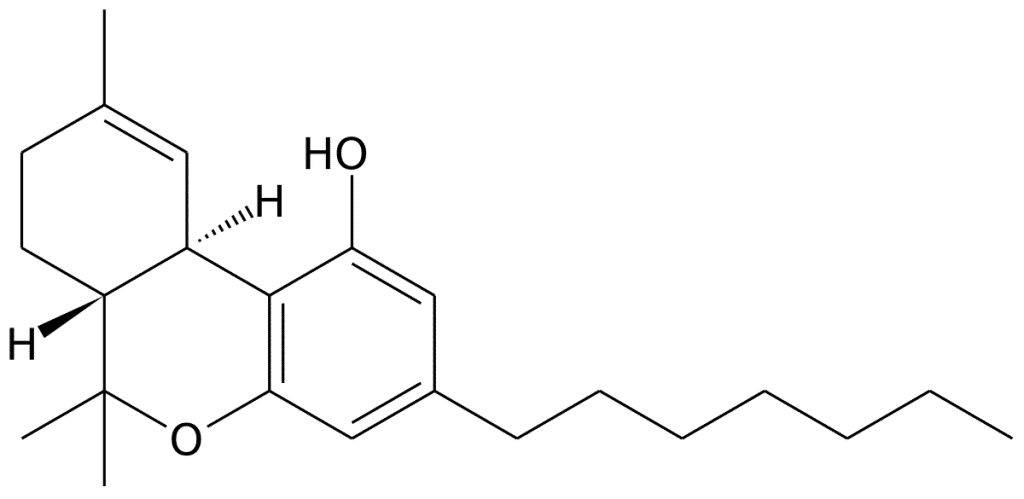
What is THCP?
Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabiphoral, or THCP, is a cannabinoid closely related to THC and present in very low concentrations in the cannabis plant.
According to the researchers who discovered it, THCP interacts with the endocannabinoid system in a similar way to THC, but with a much greater affinity for cannabinoid receptors. The research revealed that THCP binds to CB1 receptors up to 33 times more often than traditional THC, meaning that THCP is potentially up to 33 times more potent than THC.
What makes THCP unique are its long alkyl side chains: the chain of carbon atoms is much longer than that of traditional THC (seven carbons versus five). This enables the cannabinoid to attach more firmly to receptors throughout the body. As a result, a much smaller amount of THCP is needed to influence the various functions governed by the endocannabinoid system (ECS) to achieve the same effect as THC.
Potential uses and benefits
THCP is still new to the cannabis world, and no studies currently exist beyond the observations made by the original team who discovered this cannabinoid. Despite this, the evidence and potential medical applications are promising.
THCP could offer greater pain relief to patients who require high levels of THC for their care, such as those currently usingCBD oil to reduce cancer-related pain. Higher levels of THC-P could also produce sedative effects similar to high doses of THC, and are potentially capable of relievinginsomnia or reducing intractable pain.
However, there is no solid evidence of exactly how THC-P affects humans, or which strains might contain higher levels of this cannabinoid. Furthermore, while many have described THCP as having a more potent or "pronounced" effect than THC, there is no definitive proof that this cannabinoid is more potent when consumed.
Potential risks and side effects of THC-P
In the absence of available research, patients should exercise great caution when considering THCP as a potential drug until more information is available.
THCP is 33 times more capable of binding to CB1 receptors than THC, which means that greater psychoactivity is involved, even with smaller doses. You could take too much THCP and experience undesirable side effects such as dry mouth, dizziness or lethargy.
It should also be remembered that THCP is generally only present in small concentrations in cannabis. Consequently, it's hard to say what impact this cannabinoid has on the overall effect of cannabis. It is theorized that THCP may be one of the reasons why some varieties of cannabis are much more potent than others, despite similar or lower THC concentrations. However, there is no definitive proof of this concept.
Is THCP legal in France?
THCP is one of the most recently discovered cannabinoids, and remains largely unexplored. The question of its legality therefore remains uncertain. It is not classified as a controlled substance, but neither is its marketing explicitly authorized. Currently, in France, legal uncertainty allows the sale of products containing THCP, provided the THC content is less than 0.3%. However, as with all cannabinoids, legislation can vary from country to country.
THC vs THC-P: What are the differences between these components of cannabis?
Chemically, delta 9 - THCP resembles THC, except that it has a slightly longer carbon side chain.
While THC has 5 carbon atoms in its molecular structure, THC-P has 7.
These extra atoms increase its affinity with CB1 and CB2 receptors in our bodies. As a result, THCP reaches CB1 receptors 30 times faster than THC, and CB2 receptors 5 to 10 times faster. Its extended structure also enables THC-P to bind more readily to the receptor, giving it greater potency and more immediate effects than THC.
Would you like to buy THCP? Discover our flowers and other products in our online store.
Discover our Lemon Haze Ultra: https:// lordofcbd.fr/product/lemon-haze-ultra-thcp-6/
Comments are closed












2 Responses to "THCP Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabiphoral, what is it?"